图存在负权边的情况下,可以使用Bellman Ford算法和最短路径快速算法Shortest Path Faster Algorithm, SPFA
迭代 k 次后,此时 dist[i] 数组表示从源点经过不超过 k 条边到顶点 i 的最短距离
Bellman Ford算法
n 代表图的顶点数量, m 代表图的边的数量
时间复杂度 O(nm)
算法流程
迭代 n - 1 次
- 遍历所有的边 edge<a→b> ,执行松弛操作
- 更新 dist 数组, dist[b]=min{dist[b], dist[a]+weight<a→b>}
算法意义
关于迭代次数
迭代 k 次后,此时 dist[i] 数组表示从源点经过不超过 k 条边到顶点 i 的最短距离
换句话说,第 k 次迭代时,如果 dist[i] 数组某些点更新了,说明存在长度为 k 的最短路径
此原理可用来检测一个图是否存在「负权回路」
例如,第 n 次迭代时,如果 dist[] 数组中 dist[2] 更新了,说明存在长度为 n 的 orig→2 的最短路径
路径长度为 n ,即 n 条边,意味着路径上有 n+1 个点,根据抽屉原理,此路径一定存在环,且一定是负权环
ps: 检测负权回路,一般用 SPFA 算法来做
Tips
1.
全部更新完毕后,对于任意的边 edge<a→b>
均存在 dist[b]≤dist[a]+weight<a→b>
上述不等式也称作「三角不等式」
2.
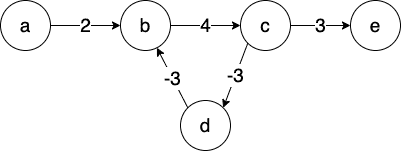
如果存在「负权回路」,最短路径可能不存在
例如:
从 a 到 e ,最短路径长度理论上是 −∞
![example.drawio]()
3.
一般来说,SPFA优于Bellman Ford算法
但是Bellman Ford可以用来解决「有边数限制」的最短路径问题
代码实现
核心代码
注意,每次迭代开始前,要先对 dist[] 数组进行备份
避免松弛操作时,使用本轮迭代更新后的 dist[] 数组
原理同动态规划:使用滚动数组降低空间占用#注意事项
以下是邻接表存储的实现方式
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
| int[] bellmanFord() {
Arrays.fill(dist, INF);
dist[1] = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < k; ++i) {
backup = Arrays.copyOf(dist, n + 1);
for (int j = 1; j <= n; ++j) {
for (int t = h[j]; t != -1; t = ne[t]) {
int a = j, b = e[t], c = w[t];
dist[b] = Math.min(dist[b], backup[a] + c);
}
}
}
return dist;
}
|
有边数限制的最短路问题
acwing 853. 有边数限制的最短路
给定一个 n 个点 m 条边的有向图,图中可能存在重边和自环,边权可能为负数。
请你求出从 1 号点到 n 号点的最多经过 k 条边的最短距离,如果无法从 1 号点走到 n 号点,输出 impossible。
注意:图中可能存在负权回路
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
| import java.util.*;
import java.io.*;
class Main{
static final int N = 510;
static final int M = 10010;
static final int INF = 0x3f3f3f3f;
static int[] h = new int[N];
static int[] e = new int[M];
static int[] ne = new int[M];
static int[] w = new int[M];
static int idx;
static int[] dist = new int[N];
static int[] backup = new int[N];
static int n, m, k;
static BufferedReader cin = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
String[] str = cin.readLine().split("\\s+");
n = Integer.parseInt(str[0]); m = Integer.parseInt(str[1]); k = Integer.parseInt(str[2]);
int a, b, c;
Arrays.fill(h, -1);
for (int i = 0; i < m; ++i) {
str = cin.readLine().split("\\s+");
a = Integer.parseInt(str[0]); b = Integer.parseInt(str[1]); c = Integer.parseInt(str[2]);
add(a, b, c);
}
bellmanFord();
cin.close();
}
static void bellmanFord() {
Arrays.fill(dist, INF);
dist[1] = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < k; ++i) {
backup = Arrays.copyOf(dist, n + 1);
for (int j = 1; j <= n; ++j) {
for (int t = h[j]; t != -1; t = ne[t]) {
int a = j, b = e[t], c = w[t];
dist[b] = Math.min(dist[b], backup[a] + c);
}
}
}
if (dist[n] > INF / 2) System.out.println("impossible");
else System.out.println(dist[n]);
}
static void add(int a, int b, int c) {
e[idx] = b;
ne[idx] = h[a];
w[idx] = c;
h[a] = idx++;
}
}
|
📔博文图谱
提及本博文的链接